What is 555 timer (part-1)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Introduction to 555 timer -
555 timer ic is extremely mainstream ic and it is helpful in the circumstance related applications. Presently, this 555 timer ic is accessible in endless bundles. But here we are going to talk about the 8pin DIP package. 
Image source - Google | image by - snappyGoat
Pin Diagram-
if you see the pin diagram, then the pin diagram will look like this. And here is the corresponding name of each pin. Along these lines, we should quickly observe the depiction of eachpin and how about we additionally observe the inside square chart of this 555 timer.So, this is the internal block diagram ofthis 555 timer ic.The first one is the voltage divider circuit. Then the next block is the comparators. And if you see, the output of the comparatoris going to the flip-flop circuit. The flip-flop is the third block.
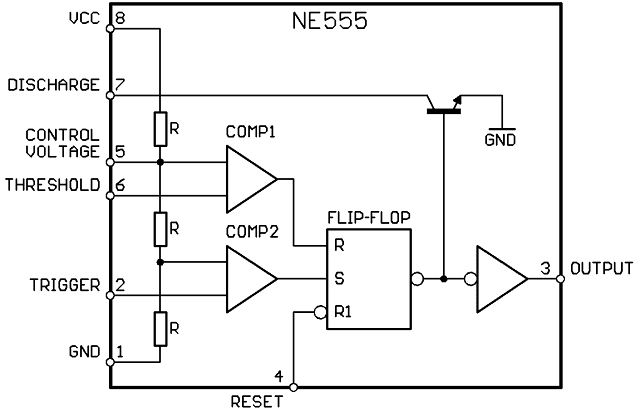
Image Source - Google | Image by - wikimediacommmons
there is a discharge circuit for the discharging purpose. And then after the last block is the outputdriver circuit. So, these are the basic blocks of this 555timer ic.In this way, individually we will see the capacity ofeach block.And at the same time, we will also understandthe purpose of individual pins.Presently, here the reason for this pin number 1,3 and 8 is quite direct.So, let's first of all talk about these threepins. so, in this 555 timer ic, the pin number 8is the supply voltage pin. And usually, the supply voltage in the rangeof 4.5 to 15V is applied at this pin. And the pin number 1 is the ground pin. And it is connected to the circuit ground. then if you see the third pin, the pin number3 is the output pin.
so, this pin is capable of driving the TTLloads and it can source or sink up to the 200 mA of current. Now, to understand the purpose of the restof the pins, first of all, let's understand the working of each block. So, as I said, the first block of this 555timer ic is the voltage divider circuit. Now, if you see over here, the voltages attwo nodes are going to the comparator.Further more, here we are accepting that the operation-amp which is utilized as a comparator is an ideal operation-amp. So, no current is flowing into the op-ampterminals. So, we can say that from this supply voltage,the current is flowing only through these three resistors.Also, that is the reason we can straightforwardly apply the voltagedivider rule.
So, by applying the rule we can say that thevoltage at this node will be equal to 2R*Vcc/(2R+R). Or we can say that the voltage at this nodeis equal to (2/3)Vcc. And this voltage is given as a reference tothis first comparator.So also, the voltage at this node can befound utilizing the voltage divider rule.So, the voltage at this node will be equalto R*Vcc/(R+2R) Or we can say that it is equal to (1/3) Vcc.Now, if you see over here, the other two pinswhich are going to this comparator is threshold and trigger pins. So, these two pins are the input pins. And by changing the voltage at these two pins,we can change the output of this comparator. So, if you see over here, the inverting nodeof this first comparator is at the 2/3 Vcc voltage. So, whenever this threshold voltage goes abovethis (2/3)Vcc voltage then, the output of the comparator will become high voltage. And similarly, if we talk about this secondcomparator, then whenever this trigger input goes below this (1/3)Vcc voltage, at thattime output of this second comparator will become high voltage.
So usually, this trigger voltage used to beat the supply voltage and whenever we want to change the state of the comparator, thenthe trigger signal is changed in a such a way that the output at this pin number 2 goes below this (1/3) Vcc voltage. Now, let's see whenever the output of this, changes then how it affects the other circuitry. So, if you see, the output of this comparatoris given to the flip-flop circuit. So, if you observe over here, the used flip-flopin the 555 timer ic is the RS flip-flop. So, let's see the truth table of this R-Sflip-flop. Now, as this R-S flip-flop is a digital circuit,so we are considering the input voltage to the flip-flop as either logic 1 or logic 0. 
Image source - Google | image by - Wikimediacommons
So from the truth table as you can see, wheneverboth inputs are logic 0 then the output of this flip-flop will be the same as the previousstate. It means that before applying this two inputs,if previously the output is either 0 or 1, then after applying these two inputs the outputwill remain the same. On the other hand, if the input to this S-Rflip-flop is 0 and 1 respectively, at that time irrespective of the previous output theflip-flop will get reset to the logic 0. And likewise, whenever S is 1 and R is 0,then irrespective the previous state of the flip-flop, the flip-flop will get set to thelogic 1. And whenever both inputs are logic '1' at that time the output is undefined.In this way, here we are just intrigued by these two conditions.So, for a moment let's assume that this triggersignal is at Vcc voltage. It means that the output of the second comparatoris at logic 0. Or we can say that, this S=0.Presently, at first we should accept that this threshold voltage is not as much as this reference voltage, that is (2/3) Vcc. And at that time, the output of this firstcomparator will be also equal to 0. So, in this case, the output of the flip-flopwill remain as it is Now, whenever this threshold voltage goes above this (2/3)Vcc voltage,then the output of the first comparator will become logic 1. Along these lines, around then the output of the flip-flop will be equivalent to 0. In this way, independent of the past state, now the output of the flip-flop is zero.And because of that, the output of this 555timer will also become zero.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Comments
Post a Comment